How Does The Fed Control The Money Supply In The Us
Agreement Money and Financial Institutions
131 The Federal Reserve System
- How does the Federal Reserve manage the money supply?
Before the twentieth century, in that location was very little government regulation of the U.S. financial or monetary systems. In 1907, however, several big banks failed, creating a public panic that led worried depositors to withdraw their coin from other banks. Soon many other banks had failed, and the U.Due south. banking arrangement was near plummet. The panic of 1907 was and then severe that Congress created the Federal Reserve System in 1913 to provide the nation with a more stable budgetary and banking system.
The Federal Reserve Arrangement (usually called the Fed) is the central banking company of the U.s.a.. The Fed's primary mission is to oversee the nation's budgetary and credit organization and to back up the ongoing operation of America'due south private-cyberbanking system. The Fed's actions affect the interest rates banks charge businesses and consumers, help keep inflation under control, and ultimately stabilize the U.Due south. fiscal system. The Fed operates equally an independent government entity. Information technology derives its potency from Congress but its decisions do not accept to be canonical by the president, Congress, or any other government branch. All the same, Congress does periodically review the Fed's activities, and the Fed must work within the economic framework established by the government.
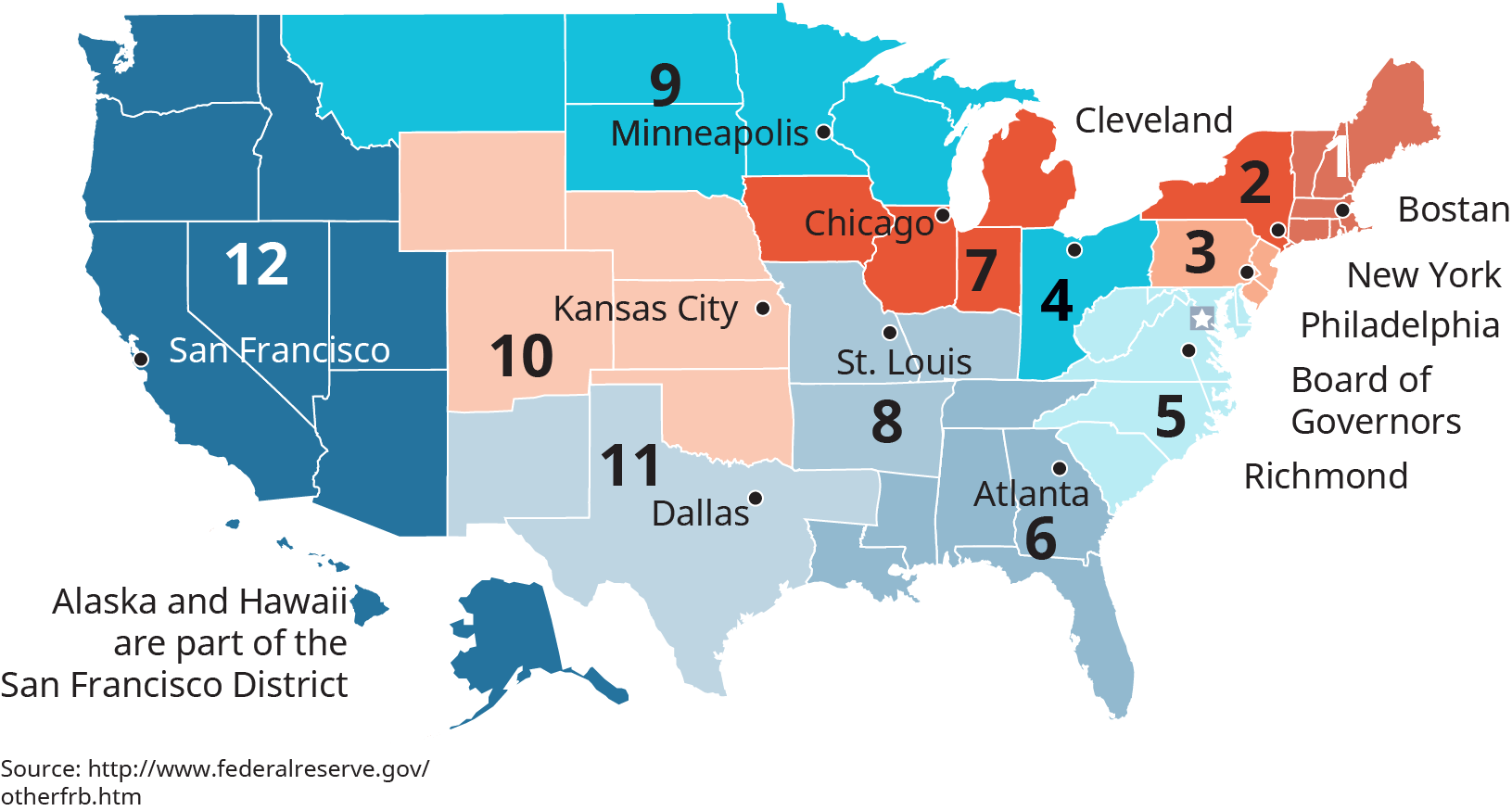
The Fed consists of 12 district banks, each roofing a specific geographic area. (Figure) shows the 12 districts of the Federal Reserve. Each district has its own bank president who oversees operations within that district.
Originally, the Federal Reserve Organization was created to command the money supply, deed as a borrowing source for banks, agree the deposits of member banks, and supervise banking practices. Its activities have since broadened, making it the about powerful financial establishment in the U.s.a.. Today, four of the Federal Reserve System'southward nearly important responsibilities are conveying out monetary policy, setting rules on credit, distributing currency, and making bank check clearing easier.
Federal Reserve Districts and Banks
Source: "Federal Reserve Banks," https://www.richmondfed.org, accessed September 7, 2017.
Conveying Out Monetary Policy
The virtually important part of the Federal Reserve System is carrying out budgetary policy. The Federal Open Marketplace Committee (FOMC) is the Fed policy-making body that meets eight times a year to brand monetary policy decisions. It uses its power to modify the money supply in club to control inflation and interest rates, increment employment, and influence economic activity. Three tools used past the Federal Reserve System in managing the coin supply are open market operations, reserve requirements, and the disbelieve rate. (Figure) summarizes the short-term effects of these tools on the economy.
Open market operations—the tool nigh oftentimes used by the Federal Reserve—involve the buy or auction of U.South. government bonds. The U.S. Treasury bug bonds to obtain the extra money needed to run the government (if taxes and other revenues aren't plenty). In event, Treasury bonds are long-term loans (five years or longer) fabricated by businesses and individuals to the regime. The Federal Reserve buys and sells these bonds for the Treasury. When the Federal Reserve buys bonds, information technology puts money into the economy. Banks have more money to lend, so they reduce interest rates, which generally stimulates economic activeness. The opposite occurs when the Federal Reserve sells government bonds.
| The Federal Reserve System's Monetary Tools and Their Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool | Action | Effect on Money Supply | Result on Interest Rates | Effect on Economic Activity |
| Open market operations | Buy regime bonds | Increases | Lowers | Stimulates |
| Sell government bonds | Decreases | Raises | Slows Down | |
| Reserve requirements | Enhance reserve requirements | Decreases | Raises | Slows Down |
| Lower reserve requirements | Increases | Lowers | Stimulates | |
| Discount charge per unit | Raise discount rate | Decreases | Raises | Slows Down |
| Lower discount rate | Increases | Lowers | Stimulates | |
Banks that are members of the Federal Reserve System must hold some of their deposits in cash in their vaults or in an business relationship at a district banking company. This reserve requirement ranges from 3 to 10 percent on different types of deposits. When the Federal Reserve raises the reserve requirement, banks must hold larger reserves and thus accept less coin to lend. As a result, involvement rates rise, and economic activeness slows downward. Lowering the reserve requirement increases loanable funds, causes banks to lower interest rates, and stimulates the economy; however, the Federal Reserve seldom changes reserve requirements.
The Federal Reserve is chosen "the broker's depository financial institution" because it lends money to banks that need information technology. The interest rate that the Federal Reserve charges its member banks is chosen the discount rate. When the discount rate is less than the cost of other sources of funds (such as certificates of eolith), commercial banks infringe from the Federal Reserve and so lend the funds at a higher charge per unit to customers. The banks turn a profit from the spread, or difference, between the charge per unit they charge their customers and the charge per unit paid to the Federal Reserve. Changes in the discount charge per unit usually produce changes in the interest rate that banks charge their customers. The Federal Reserve raises the discount rate to dull down economic growth and lowers it to stimulate growth.
Setting Rules on Credit
Some other activity of the Federal Reserve Organization is setting rules on credit. Information technology controls the credit terms on some loans made by banks and other lending institutions. This ability, called selective credit controls, includes consumer credit rules and margin requirements. Consumer credit rules establish the minimum down payments and maximum repayment periods for consumer loans. The Federal Reserve uses credit rules to wearisome or stimulate consumer credit purchases. Margin requirements specify the minimum amount of cash an investor must put upwardly to buy securities or investment certificates issued by corporations or governments. The balance of the purchase cost can be financed through borrowing from a bank or brokerage firm. By lowering the margin requirement, the Federal Reserve stimulates securities trading. Raising the margin requirement slows trading.
Distributing Currency: Keeping the Cash Flowing
The Federal Reserve distributes the coins minted and the paper coin printed past the U.South. Treasury to banks. Most paper coin is in the form of Federal Reserve notes. Wait at a dollar bill and you lot'll see "Federal Reserve Notation" at the summit. The large letter of the alphabet seal on the left indicates which Federal Reserve Bank issued information technology. For example, bills bearing a D seal are issued by the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, and those with an L seal are issued by the San Francisco commune bank.
Making Cheque Clearing Easier
Another important activeness of the Federal Reserve is processing and clearing checks between fiscal institutions. When a cheque is cashed at a financial establishment other than the i belongings the account on which the bank check is fatigued, the Federal Reserve's organization lets that financial institution—even if distant from the institution holding the business relationship on which the cheque is drawn—quickly convert the check into cash. Checks fatigued on banks inside the same Federal Reserve commune are handled through the local Federal Reserve Bank using a serial of accounting entries to transfer funds between the financial institutions. The process is more complex for checks candy between different Federal Reserve districts.
The fourth dimension between when the check is written and when the funds are deducted from the check writer's account provides float. Float benefits the check author by allowing it to retain the funds until the check clears—that is, when the funds are actually withdrawn from its accounts. Businesses open accounts at banks around the country that are known to have long check-clearing times. By "playing the float," firms tin can continue their funds invested for several actress days, thus earning more money. To reduce this do, in 1988 the Fed established maximum check-clearing times. However, as credit cards and other types of electronic payments have get more pop, the utilise of checks continues to pass up. Responding to this turn down, the Federal Reserve scaled back its check-processing facilities over the past decade. Current estimates advise that the number of check payments has declined by two billion annually over the last couple of years and volition continue to do then equally more people apply online banking and other electronic payment systems.
"The Federal Reserve Payments Study 2016," https://www.federalreserve.gov, accessed September 7, 2017; Brad Kvederis, "The Paper Cheque Lives: Why the Check Decline Slowed in 2016," http://fi.deluxe.com, January 19, 2017.
Managing the 2007–2009 Financial Crunch
Much has been written over the past decade almost the global financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2009. Some advise that without the Fed's intervention, the U.S. economy would take slipped deeper into a financial depression that could take lasted years. Several missteps by banks, mortgage lenders, and other financial institutions, which included approval consumers for home mortgages they could not afford and then packaging those mortgages into high-gamble fiscal products sold to investors, put the U.South. economy into serious financial trouble.
"BLS Spotlight on Statistics: The Recession of 2007–2009," http://world wide web.bls.gov/spotlight, accessed September 7, 2017.
In the early 2000s, the housing industry was booming. Mortgage lenders were signing up consumers for mortgages that "on newspaper" they could afford. In many instances, lenders told consumers that based on their credit rating and other financial data, they could easily take the next stride and buy a bigger house or maybe a vacation habitation because of the availability of mortgage money and low interest rates. When the U.S. housing bubble burst in tardily 2007, the value of real estate plummeted, and many consumers struggled to pay mortgages on houses no longer worth the value they borrowed to buy the properties, leaving their real estate investments "underwater." Millions of consumers simply walked away from their houses, letting them get into foreclosure while filing personal bankruptcy. At the same time, the overall economy was going into a recession, and millions of people lost their jobs as companies tightened their belts to attempt to survive the financial upheaval affecting the United States every bit well as other countries across the globe.
"Predatory Lending," The Economist, https://www.economist.com, accessed September vii, 2017; Steve Denning, "Lest Nosotros Forget: Why Nosotros Had a Fiscal Crunch," Forbes, http://world wide web.forbes.com, November 22, 2011.
In add-on, several leading fiscal investment firms, particularly those that managed and sold the high-risk, mortgage-backed financial products, failed quickly because they had not gear up aside enough money to comprehend the billions of dollars they lost on mortgages at present going into default. For instance, the venerable financial company Bear Stearns, which had been a successful business for more than than 85 years, was eventually sold to JP Morgan for less than $x a share, even after the Federal Reserve made more than $50 billion dollars available to help prop upward financial institutions in trouble.
Kimberly Amadeo, "What Is As well Large to Fail? With Examples of Banks," The Residue, https://www.thebalance.com, accessed September 7, 2017; John Maxfield, "A Timeline of Acquit Stearns' Downfall," The Motley Fool, https://world wide web.fool.com, accessed September vii, 2017.
After the collapse of Conduct Stearns and other firms such as Lehman Brothers and insurance behemothic AIG, the Fed fix a special loan programme to stabilize the banking system and to keep the U.South. bond markets trading at a normal pace. It is estimated that the Federal Reserve fabricated more than $nine trillion in loans to major banks and other fiscal firms during the two-year crisis—not to mention bailing out the automobile industry and ownership several other firms to proceed the financial organization afloat.
Chris Isidore, "Fed Made $9 Trillion in Emergency Overnight Loans," CNN Coin, http://money.cnn.com, accessed September vii, 2017.
As a result of this financial meltdown, Congress passed legislation in 2010 to implement major regulations in the fiscal industry to foreclose the future collapse of financial institutions, every bit well to put a check on abusive lending practices by banks and other firms. Among its provisions, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Human activity (known every bit Dodd-Frank) created an oversight council to monitor risks that affect the financial industry; requires banks to increment their cash reserves if the quango feels the bank has too much chance in its electric current operations; prohibits banks from owning, investing, or sponsoring hedge funds, individual equity funds, or other proprietary trading operations for profit; and set up up a whistle-blower plan to reward people who come frontwards to report security and other financial violations.
Marker Koba, "Dodd-Frank Act: CNBC Explains," CNBC, https://www.cnbc.com, accessed September 7, 2017.
Some other provision of Dodd-Frank legislation requires major U.Southward. banks to submit to annual stress tests conducted past the Federal Reserve. These annual checkups determine whether banks have plenty capital to survive economic turbulence in the financial system and whether the institutions can identify and measure risk equally part of their uppercase program to pay dividends or buy back shares. In 2017, seven years after Dodd-Frank became law, all of the land's major banks passed the annual examination.
James McBride, "The Office of the U.S. Federal Reserve," Council on Foreign Relations, https://www.cfr.org, accessed September 7, 2017; Donna Borak, "For the First Time, All U.S. Banks Pass Fed's Stress Tests," CNN Money, http://money.cnn.com, June 28, 2017.
The Federal Reserve kept short-term interest rates close to 0 percent for more than than seven years, from 2009 to December 2015, every bit a consequence of the global financial crisis. At present that the economy seems to be recovering at a slow but steady pace, the Fed began to raise the involvement rate to 1.00–1.25 percentage in mid-2017. What event do higher interest rates have on the U.S. economy? (Credit: ./ Pexels/ CC0 License/✓ Free for personal and commercial employ/✓ No attribution required)

- What are the four primal functions of the Federal Reserve System?
- What iii tools does the Federal Reserve System use to manage the money supply, and how does each impact economic activity?
- What was the Fed's role in keeping the U.S. financial markets solvent during the 2007–2009 financial crisis?
Summary of Learning Outcomes
- How does the Federal Reserve manage the money supply?
The Federal Reserve System (the Fed) is an independent government agency that performs four main functions: conveying out monetary policy, setting rules on credit, distributing currency, and making check clearing easier. The three tools it uses in managing the coin supply are open up market operations, reserve requirements, and the discount rate. The Fed played a major role in keeping the U.Southward. financial arrangement solvent during the financial crunch of 2007–2009 past making more than $9 trillion available in loans to major banks and other financial firms, in addition to bailing out the auto industry and other companies and supporting congressional passage of Dodd-Frank federal legislation.
Glossary
- discount rate
- The interest charge per unit that the Federal Reserve charges its member banks.
- Federal Reserve System (Fed)
- The central depository financial institution of the United States; consists of 12 district banks, each located in a major U.S. city.
- open up marketplace operations
- The purchase or auction of U.S. government bonds by the Federal Reserve to stimulate or ho-hum down the economy.
- reserve requirement
- Requires banks that are members of the Federal Reserve Organisation to hold some of their deposits in cash in their vaults or in an account at a district bank.
- selective credit controls
- The power of the Federal Reserve to command consumer credit rules and margin requirements.
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/businessopenstax/chapter/the-federal-reserve-system/
Posted by: smithmandis.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Does The Fed Control The Money Supply In The Us"
Post a Comment